Employee Development: Once an organization has identified behavioral competencies pertinent to a particular role and level, they can benchmark their workforce against those competencies and initiate individual developmental plans accordingly. Behavioral competencies can also enable employees to identify transferable skills for career progression.
Organizational Planning: Behavioral competencies are the bedrock of all organizational planning initiatives, such as high-potential identification, succession planning, leadership development, etc.
“Behavioral competencies lie at the core of work culture and department behavior. They make an organization’s values, mission and vision more achievable. They form the core of an organization’s behavior norms.
Since every group is different, it is vital to conduct an organization-wide exercise of nailing down behavior that employees know to be important that support the six principles – trust, interdependence, genuineness, empathy, risk resolution and success. In this way, hiring, succession planning, training and development, high potential identification, appraisals and promotion are in alignment.
When an organization has determined its group behavior norms, they can be put into performance reviews, performance-related hiring questions and the onboarding process. They can also be used to build skills so that people who demonstrate these behaviors also demonstrate the skills needed to lead people. If Gallup’s research is true, organizations promote the wrong people into leadership positions more than 82% of the time. One must look to behavior as a root cause.”
– Dianne Crampton, President, TIGERS Success Series, Inc.









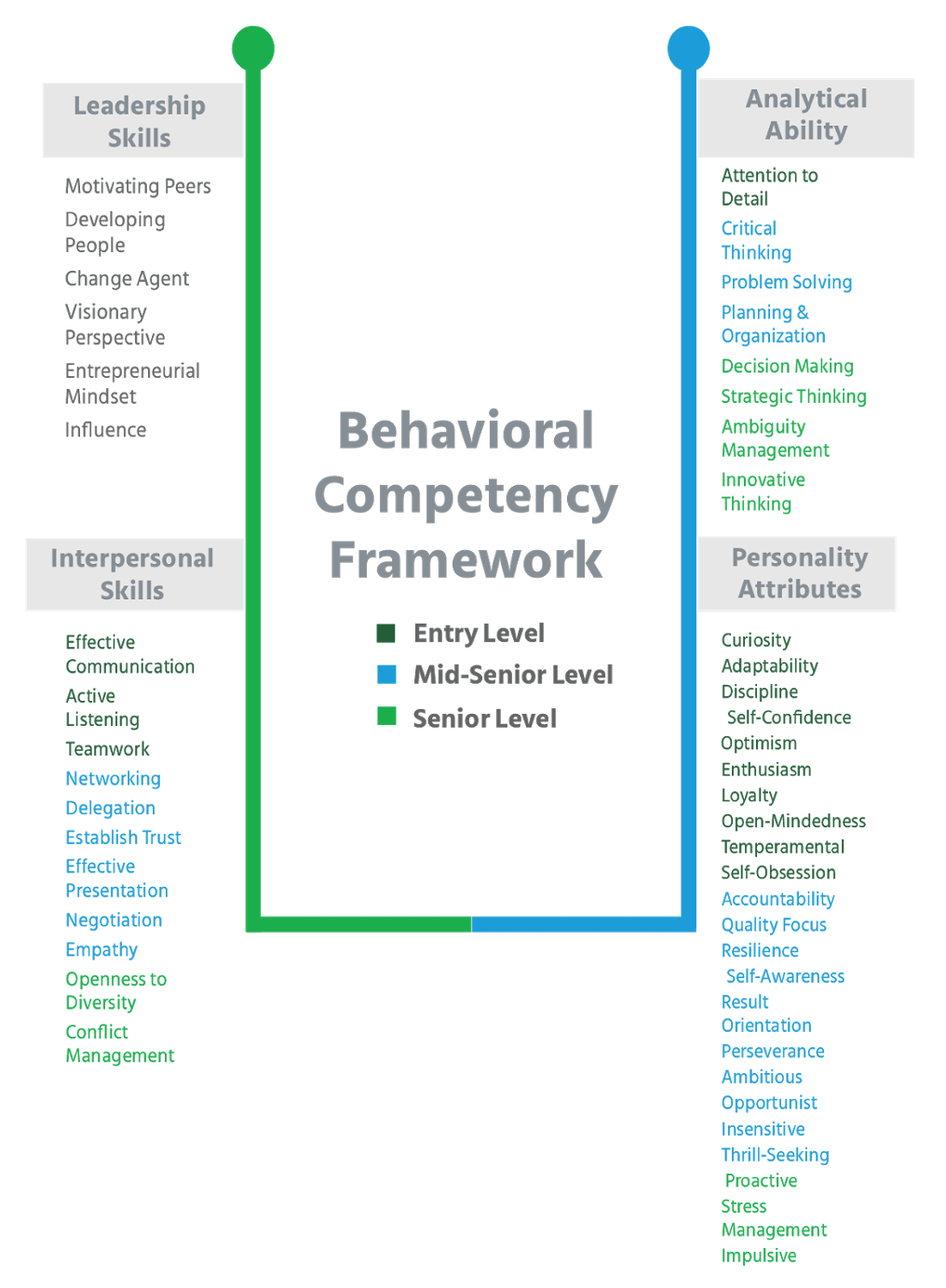
 Behavioral Competencies
Behavioral Competencies Cognitive Competencies
Cognitive Competencies Coding Competencies
Coding Competencies Domain Competencies
Domain Competencies























Would you like to comment?