Changing business and societal norms, a change in perspectives, and changes in career goals coupled with a shift in generational work ethics have combined to make work a part of a lifestyle as opposed to a distraction from it. The gig economy is on the brink of changing it all, writes Thomas Oppong, author of ‘Working in the Gig Economy’
What it means is that the work today is far more different than what it used to be a decade ago and the pattern will continue. The perception of employment, earlier, was to put money in the bank, food on the table, a secure job with some retirement income. Thanks to the shift in mindset, a career is no more about a job but a sense of accomplishment. With the ease of entry, affordability, and digital technology coming in, more men and women of all ages and independent workers from most of the fields tend to shift to the gig model of the economy.
What does this mean for businesses is the question-of-the-hour. With the ease in finding the giggers (thanks to several online platforms!), a cost-effective and efficient substitute for sudden vacancies, and more; the gig economy is a piece of great news to the businesses. Here are some of the supporting reasons:
- Reduce fixed costs- You need not pay them for benefits, training costs, onboarding costs, medical, or other HR programs; a paycheck covering just the work they are hired for. In fact, sometimes you don’t have to provide work equipment for giggers.
- Address seasonal demands- Think of Christmas time! With the bulk of orders coming in, companies like Amazon and Flipkart always need contingent workers for different domains (delivering, support, tech, etc.)
- Onboard effectively- Any organization that encounters turnover realizes that the onboarding procedure can be expensive and tedious. You don’t need to complete several HR programs that include inductions and other meetings. Onboarding freelancers is an easier way to lock in outside resources.
Companies get to outsource errands to already-trained workers and individuals, in turn, get an opportunity to work for numerous businesses in temporary positions. Well, this win-win deal is something that triggers the gig model for the future of work.
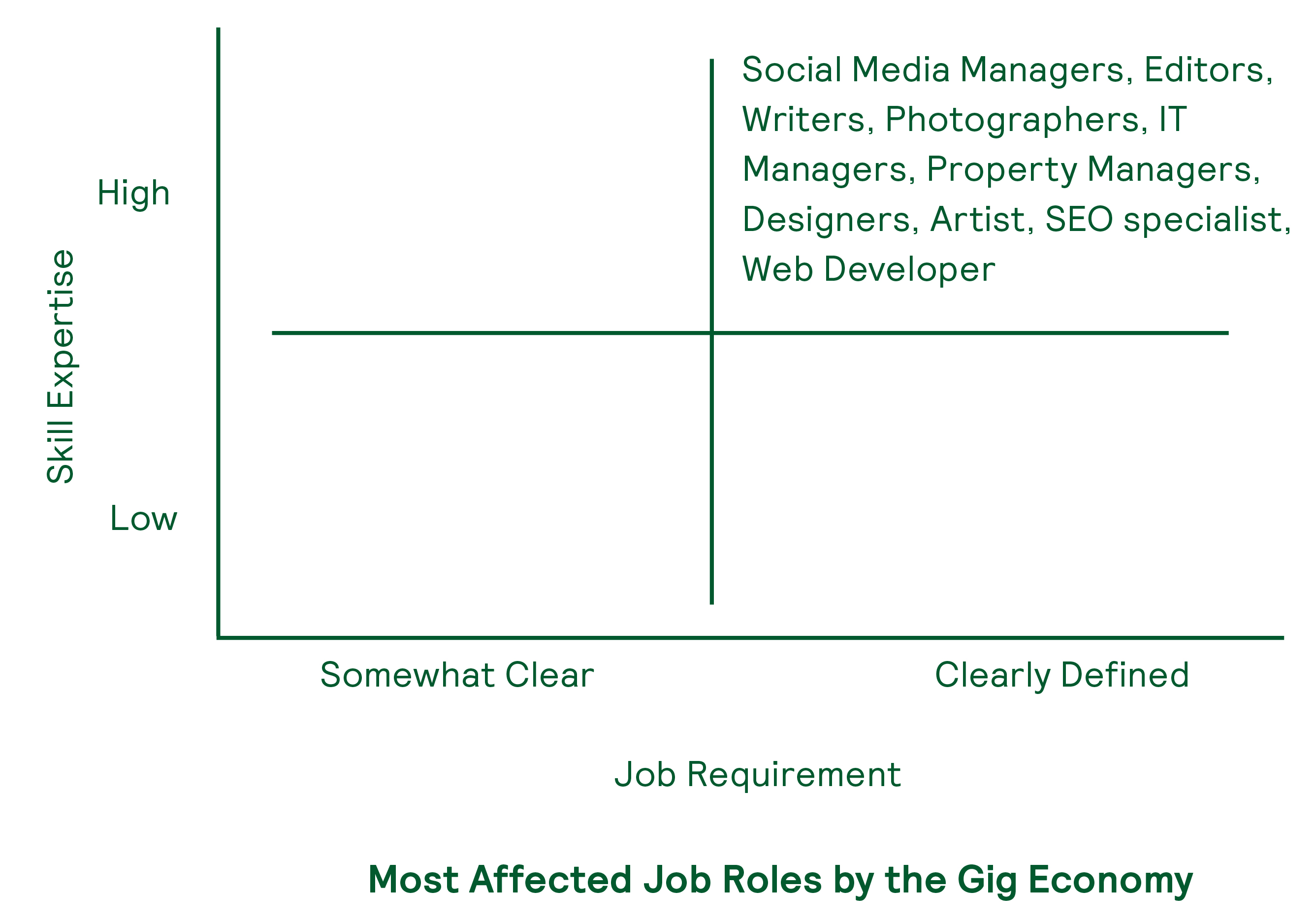
What are the Most Affected Job Roles by the Gig Economy
You see e-commerce giants like Amazon, Flipkart, Alibaba, and others. They enable anyone to join the league of merchants. Some businesses provide a chance to people with specialized skills by connecting them with clients that have such needs. Organizations will not just have to build (train) or buy (hire) talent; they will need to learn how to borrow expertise effectively.
Well, the requirement of gig workers is not just limited to these; it’s widespread in most of the sectors. For instance, photography as a job role, to a great extent, has always been into the gig model of the economy. Any organization (unless it’s a photography business) tend to hire photographers temporarily only when they need them, be it for any fest or hackathons or anything of that sort. What it means is that the role of the gig workforce comes into existence only when there is clearly defined work requirement and there are people with great expertise.
In this fast-moving world, new skills are getting introduced regularly. And the organizational structure is progressively moving towards having much more defined job roles. The mixture of both is the reason why the economy is increasingly shifting towards the gig model.
Here’s a framework that clearly describes the region of presence and growth of the gig workforce. The framework constitutes two essential parameters, which are the backbone of a contingent workforce. A higher magnitude of these parameters clearly depicts that the massive chunk of gig workers lies in this region and will continue to propel, going forward.
- Defined Work Requirement- Most of the organizations, be it small or large, opt for the contingent workforce when they have a clearly defined job role and responsibilities. For instance, companies generally go for hiring a full-time content writer, but if they need some content on a specific domain or product line quickly, they will prefer getting it done temporarily. Full job role definition also covers clearly defined financial aspects and incentive structure as well.
- Skill Expertise- If a company is hiring someone on an urgent basis to get a particular job done in a specific time, the level of expertise in that specific skill counts as a severe deciding factor. You can’t just get work done quickly without assuring that the candidate is actually capable of doing it within the given time framework.









 Behavioral Competencies
Behavioral Competencies Cognitive Competencies
Cognitive Competencies Coding Competencies
Coding Competencies Domain Competencies
Domain Competencies






















Would you like to comment?