Information Technology (IT)
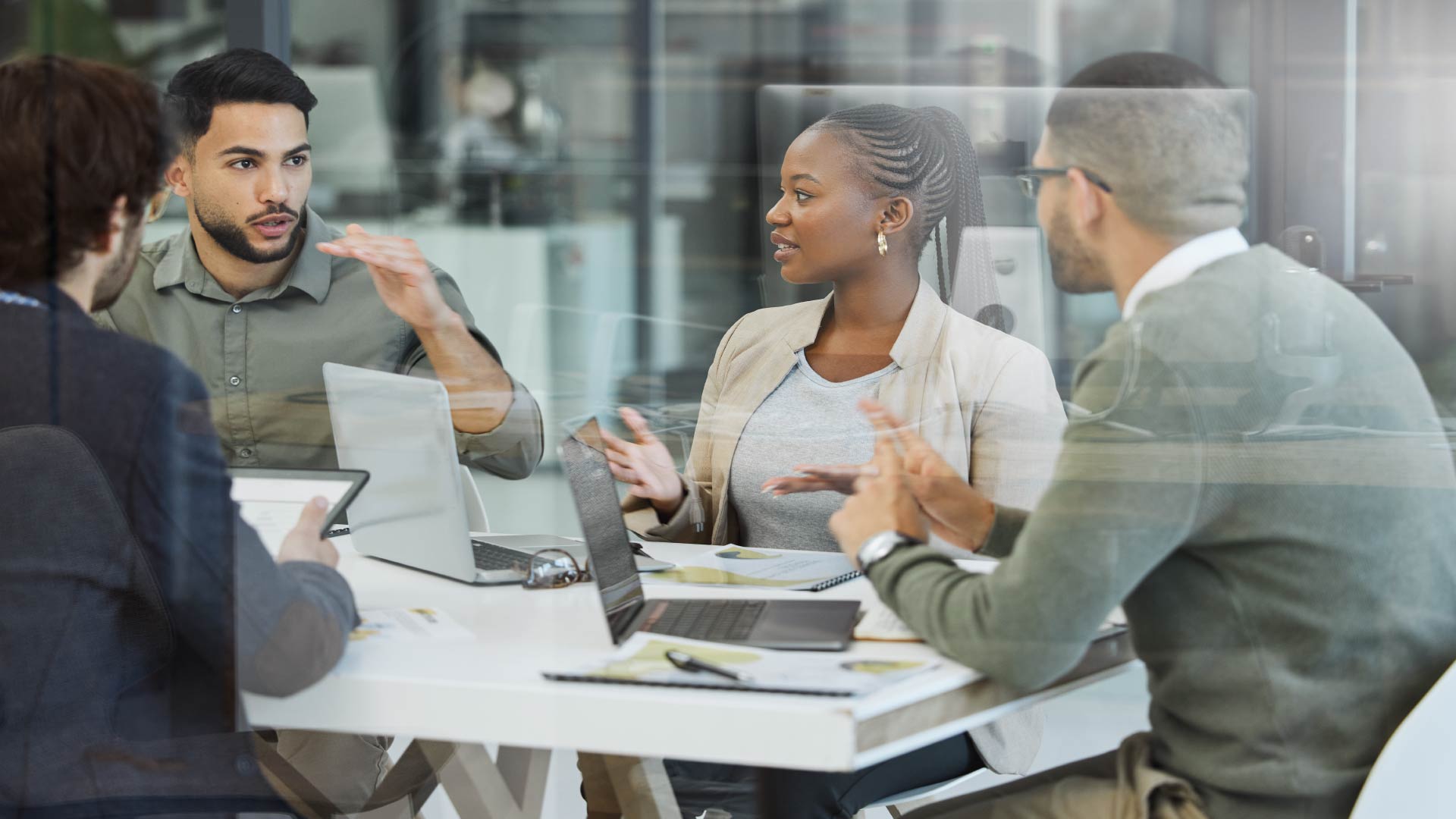
In the IT domain, technical skills are the backbone of daily operations. Proficiency in coding, network administration, and database management form the foundation for software development, IT support, and systems analysis careers. These skills ensure that systems are functional, secure, and optimized for performance.
Healthcare
Technical skills in the healthcare sector extend beyond medical knowledge. Professionals increasingly rely on tools like electronic health records (EHR) software, diagnostic imaging systems, and telemedicine platforms. Mastery of these technologies improves patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
Finance
From advanced Excel formulas to specialized accounting software, technical skills in finance are critical for managing budgets, forecasting trends, and ensuring compliance. Financial analysts, for instance, depend heavily on data visualization tools and statistical models to deliver actionable insights.
Engineering
Engineers leverage technical skills to design, build, and test projects. Whether it’s AutoCAD for civil engineers or MATLAB for mechanical engineers, these tools facilitate precision and innovation in their work.
Creative industries
Graphic designers, animators, and video editors rely on software tools to bring their ideas to life. Technical proficiency in platforms like Photoshop, Blender, and Final Cut Pro is essential for producing high-quality work that stands out.










 Behavioral Competencies
Behavioral Competencies Cognitive Competencies
Cognitive Competencies Coding Competencies
Coding Competencies Domain Competencies
Domain Competencies

















Would you like to comment?