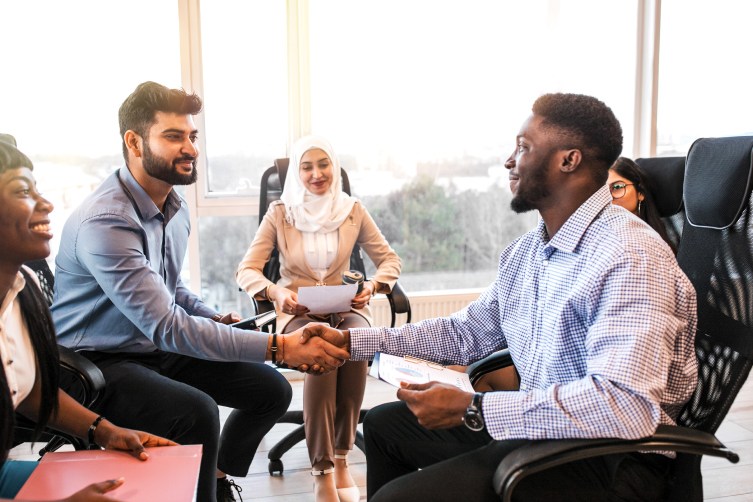
From an industry perspective, the Union Budget 2024-25 has been widely received as a positive step towards addressing the skill gap and enhancing employment opportunities. HR professionals and industry leaders collectively view these budgetary measures as crucial for building a skilled, employable, and future-ready workforce. The collaborative nature of these measures makes everyone feel included in the collective effort to shape the future of India’s workforce.
1. Alignment with industry needs
The emphasis on industry-aligned training programs and apprenticeships addresses the gap between education and employment. The collaboration between educational institutions and industries ensures that the curriculum remains relevant, thus preparing students for real-world job requirements. This alignment is expected to reduce companies’ time and resources to train new employees, leading to increased productivity.
2. Focus on digital skills
The allocation for digital skill hubs highlights the growing recognition of the importance of digital literacy in the modern job market. As industries across sectors increasingly adopt digital technologies, the demand for professionals skilled in areas such as AI, machine learning, and cybersecurity continues to rise. These hubs are expected to produce a steady stream of talented professionals proficient in these cutting-edge technologies, thereby supporting the digital transformation of businesses.
3. Support for MSMEs and startups
The HR industry views support for MSMEs and startups as critical for job creation. These entities are often the breeding grounds for innovation and new job roles. By providing financial backing, the government is promoting entrepreneurship and ensuring that these businesses can scale and create more job opportunities. The focus on startups also encourages a culture of continuous learning and skill development among employees.
4. Inclusive growth and diversity
The expanded reach of the Skill India Mission and the inclusive approach to skill development are significant steps towards promoting diversity and inclusion in the workforce. These initiatives aim to create a more balanced and equitable job market by targeting marginalized groups, women, and differently abled individuals. This inclusive growth is crucial for tapping into the full potential of the country’s human resources.
5. Enhancing higher education
The budget’s focus on higher education and research is expected to have a long-term positive impact on workforce quality. Enhanced research capabilities and international collaborations will likely lead to innovations and advancements in various fields. This translates to a more qualified and competitive talent pool for HR professionals, which is essential for sustaining economic growth and maintaining global competitiveness.










 Behavioral Competencies
Behavioral Competencies Cognitive Competencies
Cognitive Competencies Coding Competencies
Coding Competencies Domain Competencies
Domain Competencies




















Would you like to comment?