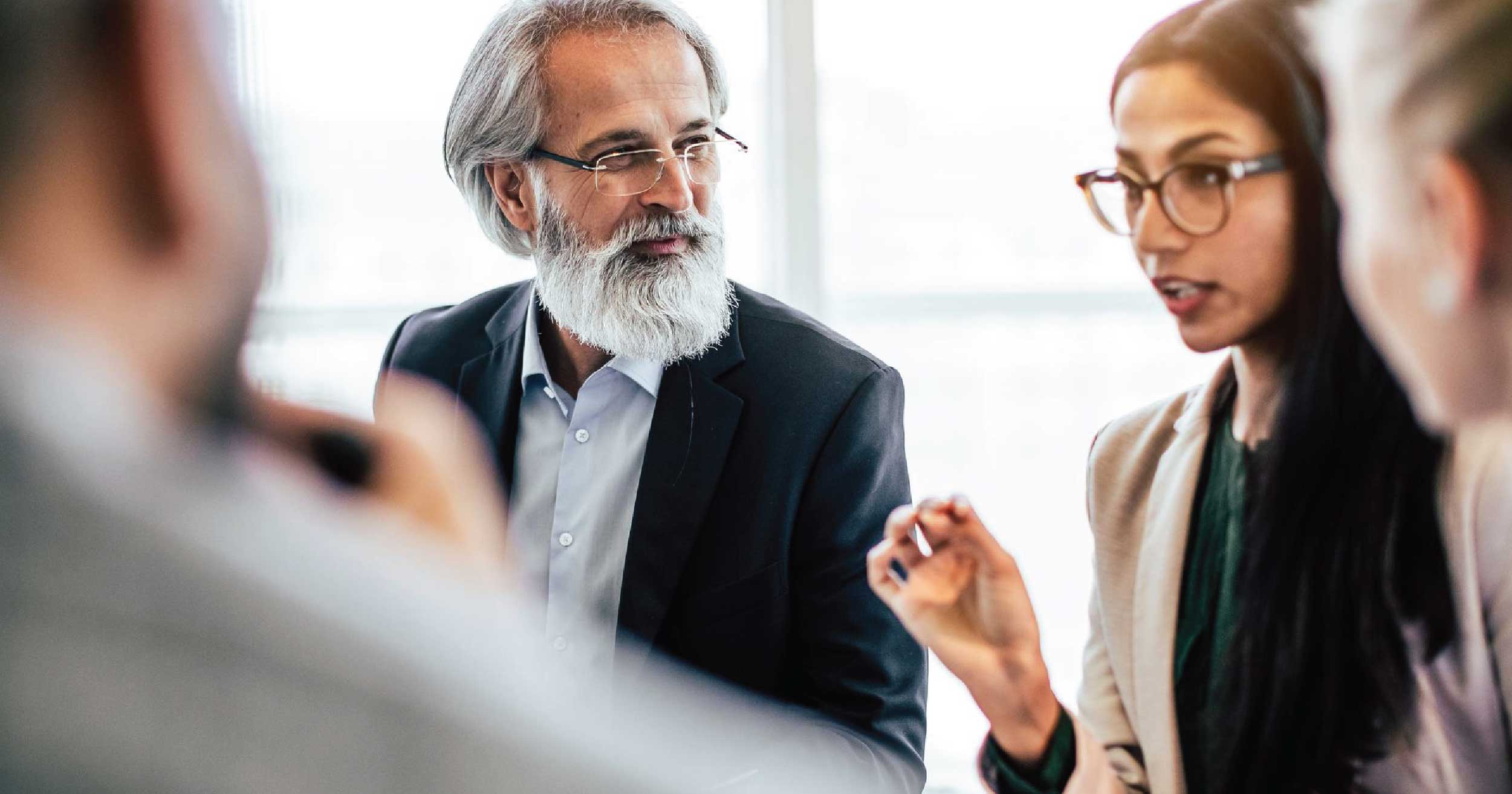
1. Offer learning opportunities for employees
Learning and development opportunities are necessary as more candidates consider them when applying for jobs. Organizations that want to attract top talent need to be able to showcase their commitment towards employee development.
In a survey conducted by TalentLMS and the Society for Human Resources, 76% of employees stated that they were more likely to stay with an organization if they were provided continuous training opportunities. Candidates are on the lookout for organizations where they are offered career-enhancing learning and development opportunities.
2. Enhance employee engagement and experience
Learning and development programs ensure that employees gain confidence in their performance and feel inspired to take more initiative towards pursuing their career aspirations. This helps boost morale, employee engagement, and job satisfaction.
3. Promote diversity, equity, inclusivity, and belonging (DEIB)
One of the primary concerns for organizations that want to instill a culture that attracts top talent and improves productivity is establishing an inclusive and equitable workplace. It is important to have employees from diverse backgrounds to promote a sense of belonging.
4. Bridge skills gaps
Keeping up with the latest technological advancements and regular shifts in the business landscape can get challenging, which is why organizations need to ensure that their employees are equipped to face these emerging challenges. Reskilling and upskilling the employees for specialized roles and offering them opportunities to develop their soft skills prepare them to adapt to changing situations, foster innovation, and be ready to meet the organization’s future needs.
5. Build a strong employer reputation
Almost everyone is looking for jobs with organizations that offer multiple learning and development opportunities for employee growth. Learning and development strategies have become a necessity for improving the employer brand. Organizations with robust learning and development initiatives in place have a strong advantage over others when it comes to attracting and hiring top talent.
6. Foster a positive company culture
Learning and development programs contribute to building a positive workplace environment and fostering team bonding. These initiatives enable group activities and learning events, like social clubs, helping teams form strong bonds.
7. Improve customer service and customer satisfaction
Customers look at the employees of an organization as experts in the field, and they expect them to be able to deliver complex information simply. Learning and development programs empower every employee to handle customer interactions with ease, ensuring that they are always up to date with all product and service information.









 Behavioral Competencies
Behavioral Competencies Cognitive Competencies
Cognitive Competencies Coding Competencies
Coding Competencies Domain Competencies
Domain Competencies